Multimask Discrete Diffusion Models for Text Generation: Principles and Applications
Tired of autoregressive text limitations? Explore multimask discrete diffusion! This article reveals how iterative refinement & bidirectional context enhance text generation. Discover models like LLaDA for more coherent and robust outputs. A new frontier in NLP!
Most of today's advanced AI text generators (like ChatGPT or other GPT models) create text one word at a time, always moving from left to right - much like how humans typically write. These are called autoregressive models. While this approach works well, it has a significant drawback: if the model makes a mistake early on, that error can snowball and affect everything that comes after.
Enter multimask discrete diffusion - a different approach that's gaining attention for addressing these limitations. Instead of generating text strictly from left to right, this method:
- Works on multiple parts of the text simultaneously
- Can look at both what comes before AND after a word to make better predictions
- Refines its output through multiple passes, improving quality with each iteration
Think of it like the difference between writing a first draft in one go versus writing an outline, then filling it in, and then revising it several times until it's polished.
How It Works: The Basics
Autoregressive Models (Traditional Approach)
Traditional text generation works like this:
- Start with a prompt: "The cat sat on the..."
- Predict the next word: "mat"
- Then predict the word after that: "while"
- And continue one word at a time: "the sun shone through the window"
This approach only uses what came before to predict what comes next.
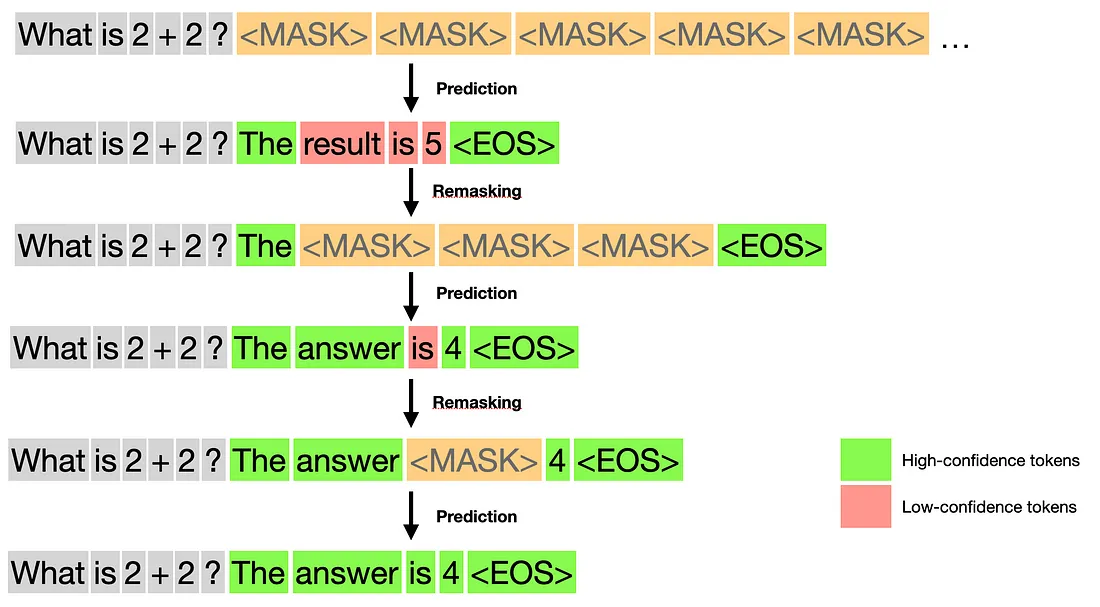
Multimask Diffusion Models (New Approach)
Multimask diffusion works differently:
- Start with masks: "The cat [MASK] on the [MASK] while the [MASK] shone through the window"
- First pass: "The cat sat on the mat while the moon shone through the window"
- Second pass: "The cat sat on the mat while the sun shone through the window"
Each pass refines the previous guess, and the model can see the entire context when making decisions.
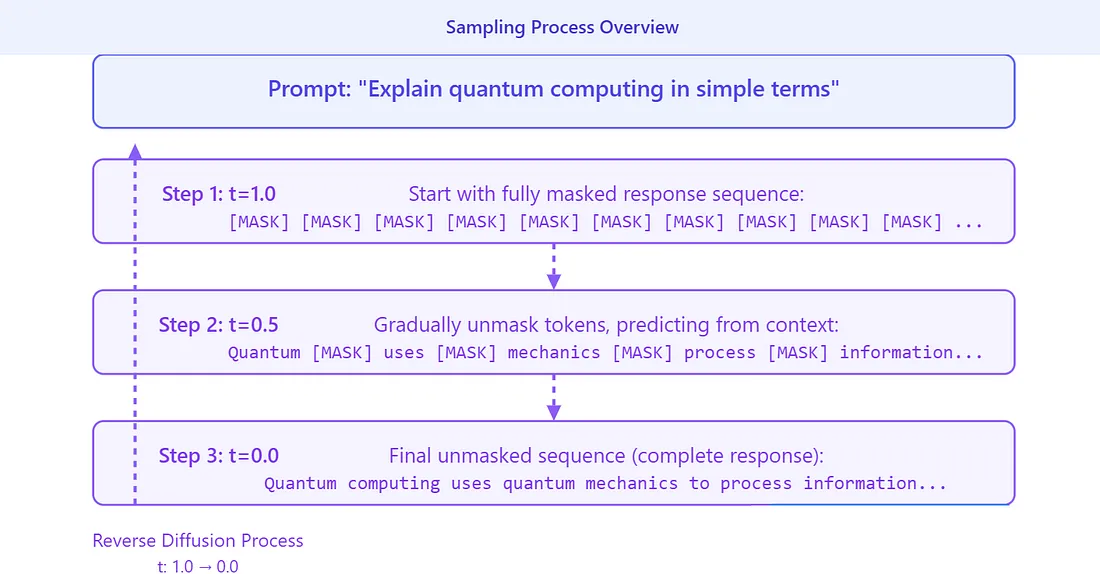
The Two-Phase Process
Multimask diffusion models work through two main phases:
1. Forward Process (Adding Noise)
This is like deliberately removing words from a complete sentence to create a fill-in-the-blank exercise:
Original: "Despite numerous setbacks during the project, the team remained resilient in their pursuit of excellence."
After adding "noise" (masking): "Despite numerous [MASK] during the project, the team remained [MASK] in their pursuit of excellence."
2. Reverse Process (Removing Noise)
This is where the magic happens. The model:
- Looks at what's left of the text
- Makes educated guesses about what should fill those blanks
- Refines its guesses over multiple steps
- Uses both left and right context to improve accuracy
The final result might be: "Despite numerous setbacks during the project, the team remained resilient in their pursuit of excellence."
Why This Method Matters: Key Advantages
Better Overall Coherence
By looking at the entire context and refining through multiple passes, diffusion models can create text that hangs together better, especially for longer pieces.
Error Correction
If a traditional model makes an early mistake, it's stuck with it. Diffusion models can "change their mind" in later passes if an early choice doesn't fit well with what comes later.
Bidirectional Understanding
Words in natural language often depend on both what came before AND what comes after. Diffusion models can see in both directions, making them more similar to how humans understand language.
The Trade-Off: Computational Costs
There's no free lunch in AI! The main drawback of multimask diffusion is that it requires:
- Multiple processing passes instead of just one
- More computing power and time
- Greater complexity in training and implementation
Researchers are actively working on solutions to make these models faster, including:
- Using fewer refinement steps
- Dynamically adjusting the number of steps based on the difficulty of the text
- Training smaller models to mimic the output of larger diffusion models
Real-World Example: Filling in the Blanks
Let's see how this works in practice with a simple example:
Input: "Despite numerous setbacks during the project, the team remained _______ in their pursuit of excellence."
A multimask diffusion model would approach this by:
-
Starting point: It might actually mask more words to consider broader context: "Despite numerous [MASK] during the project, the team remained [MASK] in their pursuit of excellence."
-
First pass: It might fill in with "challenges" and "committed"
-
Second pass: It might reconsider and choose "setbacks" and "dedicated"
-
Final pass: It settles on "setbacks" and "resilient" as the best fit for the overall meaning
This showcases how the model iteratively improves its understanding of what would make the most coherent text.
Case Study: LLaDA - Diffusion at Scale
LLaDA (Large Language Diffusion with Masking) is a cutting-edge implementation of these principles, with models containing up to 8 billion parameters. Here's what makes it special:
How LLaDA Is Trained
- Uses dynamic masking strategies during training
- Learns to predict masked words based on surrounding context
- Becomes skilled at filling in missing information in a coherent way
Benefits of LLaDA
- Creates more logically consistent text
- Has built-in mechanisms for self-correction
- Can match or exceed the performance of traditional models like LLaMA3 on certain tasks
Current Limitations
- Slower generation time compared to traditional models
- Requires more computational resources
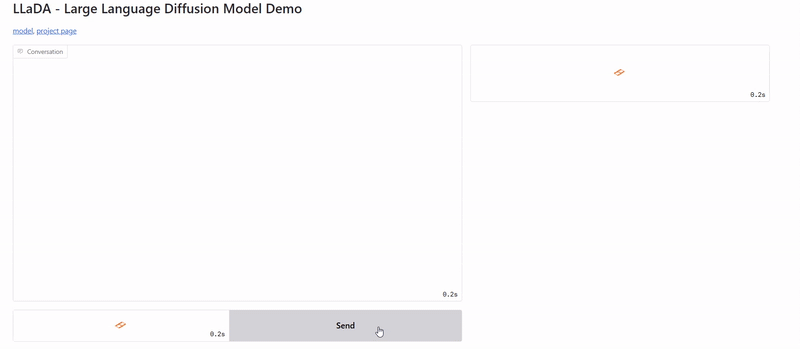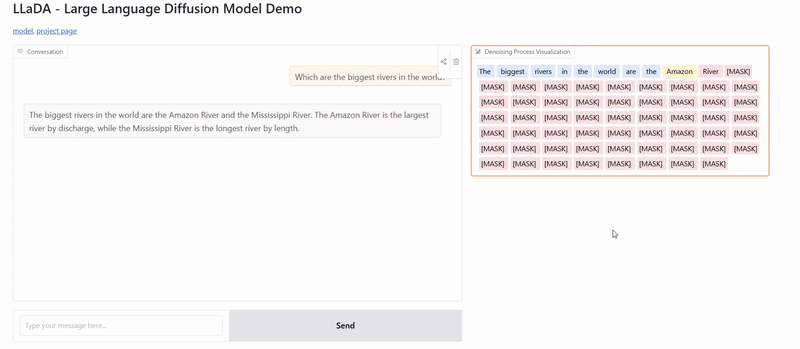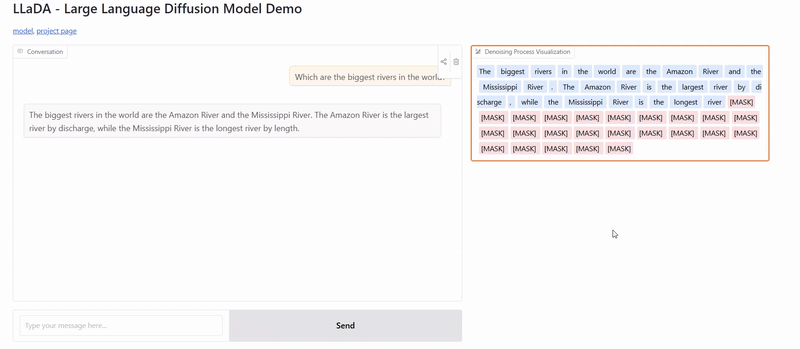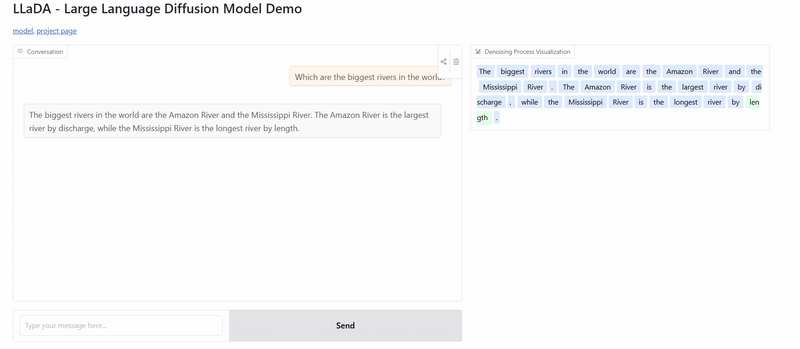
Application Example: Creating Stories
Creating longer narratives really showcases the strengths of diffusion models. Given a prompt:
Prompt: "In the heart of a bustling city, Mia discovered a mysterious book in a forgotten library. Its pages hinted at hidden secrets and untold adventures."
A multimask diffusion approach would:
- First establish key elements (characters, setting, objects)
- Then develop the narrative flow, ensuring events make logical sense
- Finally refine the language and details to create a polished story
This approach helps prevent common problems in AI-generated stories like going off-topic, repetition, or contradicting earlier statements.
Conclusion: The Future of Text Generation
Multimask discrete diffusion represents an exciting alternative to traditional text generation methods. By using iterative refinement and looking at text holistically rather than sequentially, these models offer meaningful improvements in coherence and quality.
While challenges remain in making these models faster and more efficient, ongoing research shows promise for addressing these limitations. As the technology evolves, we may see diffusion models become increasingly common in applications where text quality and coherence are paramount.
For those interested in natural language processing and AI text generation, multimask discrete diffusion is definitely a technology to watch in the coming years.